场景:修复 header 下拉菜单被 section 遮挡的问题
问题背景
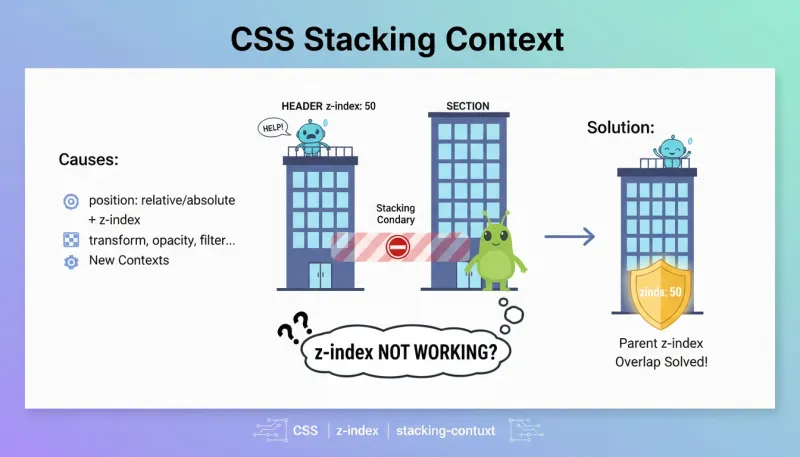
在 home.html 中,导航菜单的下拉框被页面第一个 section 遮挡了。即使下拉菜单设置了 z-index: 50,依然被覆盖。
当去掉 section 的 position: relative 后,下拉菜单又能正常显示了。
根本原因
这是 CSS 层叠上下文 的经典问题。
什么是层叠上下文?
层叠上下文是 HTML 元素在 Z 轴(垂直于屏幕方向)上的层级划分。可以理解为一个”独立的小宇宙”——内部的 z-index 只在这个小宇宙内比较,跟外部无关。
大楼类比
plaintext
12345678910111213
想象一栋大楼:
├── 1 号楼 (层叠上下文 A: header)
│ ├── A 的 1 层
│ ├── A 的 50 层 ← 下拉菜单 z-index: 50
│ └── A 的 100 层
│
├── 2 号楼 (层叠上下文 B: section)
│ ├── B 的 1 层 ← 整栋楼比 A 高,这层就能挡住 A 的 50 层
│ └── B 的 10 层
结论:A 楼里的 50 层再高,也比不过 B 楼的 1 层
因为 B 整栋楼就建在 A 楼上面实际代码
html
123456789
<!-- Header: position: relative, 没有 z-index → 创建层叠上下文 A -->
<header class="relative">
<!-- 下拉菜单 z-index: 50,只在 A 内部有效 -->
<div class="header-nav-dropdown" style="z-index: 50;">
</header>
<!-- Section: position: relative → 创建层叠上下文 B -->
<!-- B 在 DOM 中位于 A 后面,按默认顺序会覆盖 A -->
<section class="relative overflow-hidden">什么会创建层叠上下文?
| 属性 | 条件 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
position | relative/absolute + z-index 非 auto | position: relative; z-index: 1; |
position | fixed 或 sticky(无需 z-index) | position: fixed; |
opacity | 值小于 1 | opacity: 0.99; |
transform | 任意非 none 值 | transform: translateX(0); |
filter | 任意非 none 值 | filter: blur(0); |
backdrop-filter | 任意非 none 值 | backdrop-filter: blur(4px); |
isolation | isolate | isolation: isolate; |
will-change | 指定特定属性 | will-change: transform; |
contain | layout/paint/strict/content | contain: paint; |
mix-blend-mode | 非 normal 值 | mix-blend-mode: multiply; |
层叠顺序(同一上下文内,从下到上)
plaintext
1234567
7. z-index > 0 的定位元素
6. z-index: 0 / auto 的定位元素
5. inline / inline-block 元素
4. float 浮动元素
3. block 块级元素
2. z-index < 0 的定位元素
1. 背景和边框(最底层)解决方案
方案 1:给父元素加 z-index(推荐)
html
12345
<header class="relative z-50">
<!-- 整个 header 的层叠上下文优先级提高 -->
<!-- 内部的下拉菜单自然能显示在 section 上面 -->
</header>
<section class="relative">...</section>方案 2:去掉后续元素的 position
html
1234
<header class="relative">...</header>
<section class="overflow-hidden">
<!-- 不用 relative,不创建新的层叠上下文 -->
</section>方案 3:使用 isolation: isolate
html
123
<header class="relative isolate">
<!-- isolate 会创建新的层叠上下文,但不影响 z-index 值 -->
</header>常见踩坑
坑 1:父元素 z-index 低,子元素再高也没用
css
12
.parent { position: relative; z-index: 1; }
.child { position: absolute; z-index: 9999; } /* 没用!受限于 parent */坑 2:opacity 意外创建层叠上下文
css
12
.modal-overlay { opacity: 0.5; } /* 意外创建了层叠上下文 */
.modal-content { z-index: 999; } /* 被限制在 overlay 内部 */坑 3:transform 性能优化的副作用
css
1234
.parent {
transform: translateZ(0); /* 常用于开启 GPU 加速 */
/* 但这会创建层叠上下文,影响子元素的 z-index */
}坑 4:fixed 定位的元素脱离不了 transform 父元素
css
12345
.parent { transform: scale(1); }
.child {
position: fixed; /* 本应相对于视口定位 */
/* 但因为父元素有 transform,会相对于父元素定位! */
}调试技巧
Chrome DevTools
- Layers 面板:查看所有层叠上下文
- 3D View:立体化展示层叠关系
- Elements 面板:选中元素后查看 Computed 样式中的 z-index
快速定位问题
javascript
12345678910111213
// 在控制台运行,列出所有创建层叠上下文的元素
[...document.querySelectorAll('*')].filter(el => {
const style = getComputedStyle(el);
return (
style.position !== 'static' && style.zIndex !== 'auto' ||
style.position === 'fixed' ||
style.position === 'sticky' ||
parseFloat(style.opacity) < 1 ||
style.transform !== 'none' ||
style.filter !== 'none' ||
style.isolation === 'isolate'
);
}).forEach(el => console.log(el, getComputedStyle(el).zIndex));最佳实践
- Header/Navbar 永远加 z-index:
z-50或更高 - Modal/Dialog 使用高 z-index:
z-[9999]或 Portal 到 body 末尾 - 避免不必要的 position: relative:只在需要时使用
- 注意 transform/opacity 的副作用:它们会创建层叠上下文
- fixed 元素放到 body 直接子级:避免被 transform 父元素影响